Lighting Window
The Lighting window (menu: Window > RenderingThe process of drawing graphics to the screen (or to a render texture). By default, the main camera in Unity renders its view to the screen. More info
See in Glossary > Lighting Settings) is the main control point for Unity’s Global Illumination (GI) features. Although GI in Unity gives good results with default settings, the Lighting window’s properties allow you to adjust many aspects of the GI process, to customise your Scene or optimise for quality, speed and storage space as you need. This window also includes settings for ambient light, halos, cookies and fog.
Overview
The controls of the Lighting window are divided among three tabs:
The SceneA Scene contains the environments and menus of your game. Think of each unique Scene file as a unique level. In each Scene, you place your environments, obstacles, and decorations, essentially designing and building your game in pieces. More info
See in Glossary tab settings apply to the overall Scene rather than individual GameObjectsThe fundamental object in Unity scenes, which can represent characters, props, scenery, cameras, waypoints, and more. A GameObject’s functionality is defined by the Components attached to it. More info
See in Glossary. These settings control lighting effects and also optimisation options.The Global maps tab shows all of the lightmapA pre-rendered texture that contains the effects of light sources on static objects in the scene. Lightmaps are overlaid on top of scene geometry to create the effect of lighting. More info
See in Glossary Asset files generated by the GI lighting process.The Object maps tab shows previews of GI lightmap textures (including shadow masks) for the currently selected GameObject.
The window also has an Auto Generate checkbox below the displayed content. If you tick this checkbox, Unity updates lightmap data as you edit the Scene. Note that the update usually takes a few seconds rather than happening instantaneously. If you leave the Auto Generate box unticked, the Generate Lighting button to the right of the checkbox becomes active; use this button to trigger lightmap updates when you need them. Use the Generate Lighting button if you want to clear the baked data from the Scene without clearing the GI CacheThe cached intermediate files used when Unity precomputes real-time GI, and when baking Static Lightmaps, Light Probes and Reflection Probes. Unity keeps this cache to speed up computation. More info
See in Glossary.
Scene tab
The Scene tab contains settings that apply to the overall Scene, rather than individual GameObjects. The Scene tab contains several sections:
- Environment
- Realtime Lighting
- Mixed LightingA Light Mode for creating indirect lighting, shadowmasks and subtractive lighting. Indirect lighting gets baked into lightmaps and light probes. Shadowmasks and light probes occlusion get generated for baked shadows. More info
See in Glossary - Lightmapping Settings
- Other Settings
- Debug Settings
Environment
The Environmental Lighting section contains settings for the skybox, diffuse lighting and reflections.
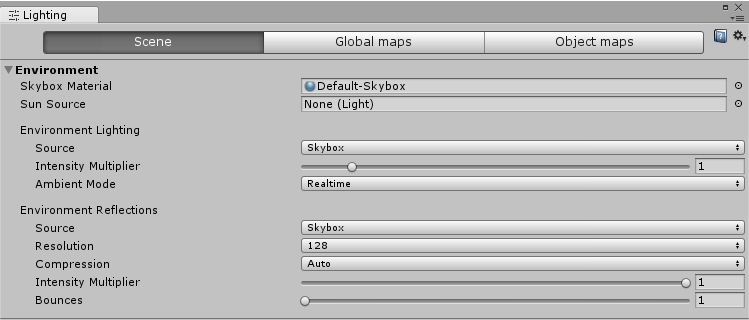
| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| Skybox Material | A skybox is a Material that appears behind everything else in the Scene to simulate the sky or other distant background. Use this property to choose the skybox Material you want to use for the Scene. The default value is the Material Default-Skybox in the Standard AssetsA collection of useful assets supplied with Unity. Unity ships with multiple Standard Asset such as 2D, Cameras, Characters, CrossPlatformInput, Effects, Environment, ParticleSystems, Prototyping, Utility, and Vehicles. More info See in Glossary. |
| Sun Source | When a procedural skybox is used, use this to specify a GameObject with a directional Light component to indicate the direction of the “sun” (or whatever large, distant light source is illuminating your Scene). If this is set to None (the default), the brightest directional light in the Scene is assumed to represent the sun. |
| Environment Lighting | These settings affect light coming from the distant environment. |
| Source | Diffuse environmental light (also known as ambient light) is light that is present all around the Scene and doesn’t come from any specific source object. Use this to define a source colour. The default value is SkyboxA special type of Material used to represent skies. Usually six-sided. More info See in Glossary. |
| Color | Select this to use a flat color for all ambient light in the Scene. |
| Gradient | Select this to choose separate colors for ambient light from the sky, horizon and ground, and blend smoothly between them. |
| Skybox | Select this to use the colors of the skybox (if specified by the Skybox Material) to determine the ambient light coming from different angles. This allows for more precise effects than Gradient. |
| Intensity Multiplier | Use this to set the brightness of the diffuse environmental light in the Scene, defined as a value between 0 and 8. The default value is 1. |
| Ambient Mode | Use this to specify the Global Illumination mode that should be used to handling ambient light in the Scene. This property is only available when both real-time lighting and baked lighting are enabled in the Scene. |
| Realtime | Choose Realtime if you want the ambient light in the Scene to be calculated and updated in real time. |
| Baked | Choose Baked if you want the ambient light to be precomputed and set into the Scene at run time. |
| Environment Reflections | These settings control global settings involved in Reflection ProbeA rendering component that captures a spherical view of its surroundings in all directions, rather like a camera. The captured image is then stored as a Cubemap that can be used by objects with reflective materials. More info See in Glossary baking, and settings affecting global reflections. |
| Source | Use this setting to specify whether you want to use the skybox for reflection effects, or a cube map of your choice. The default value is Skybox. |
| Skybox | Select this to use the skybox for reflections. If you select Skybox, an additional option called Resolution appears. Use this to set the resolution of the skybox for reflection purposes. |
| Custom | Select this to use a cube map for reflections. If you select Custom, an additional option called CubemapA collection of six square textures that can represent the reflections in an environment or the skybox drawn behind your geometry. The six squares form the faces of an imaginary cube that surrounds an object; each face represents the view along the directions of the world axes (up, down, left, right, forward and back). More info See in Glossary appears. Use this to set the cube map of the skybox for reflection purposes. |
| CompressionA method of storing data that reduces the amount of storage space it requires. See Texture Compression, Animation Compression, Audio Compression, Build Compression. See in Glossary |
Use this to define whether or not reflection textures are compressed. The default setting is Auto. |
| Auto | The reflection texture is compressed if the compression format is suitable. |
| Uncompressed | The reflection texture is stored in memory uncompressed. |
| Compressed | The texture is compressed. |
| Intensity Multiplier | The degree to which the reflection source (the skybox or cube map specified in the Reflection Source property) is visible in reflective objects. |
| Bounces | A reflection “bounce” occurs when a reflection from one object is then reflected by another object. The reflections are captured in the scene through the use of Reflection Probes. Use this property to set how many times the Reflection Probes evaluate bounces back and forth between objects. If this is set to 1, then Unity only takes the initial reflection (from the skybox or cube map specified in the Reflection Source property) into account. |
Realtime Lighting

| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| Realtime Global Illumination | If this checkbox is ticked, Unity calculates and updates the lighting in real time. See documentation on Realtime Global Illumination for more information. |
Mixed Lighting
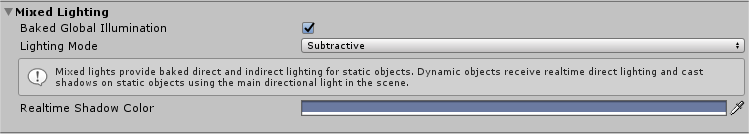
| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| Baked Global Illumination | If this checkbox is ticked, Unity precomputes the lighting and sets it into the Scene at run time. See documentation on Baked Global Illumination for more information. |
| Lighting Mode |
Lighting Mode determines the way Mixed Lights and shadows work with GameObjects in the Scene. Note: When you change the Lighting Mode, you also need to re-bake the Scene. If Auto Generate is enabled in the Lighting window, this happens automatically. If Auto Generate is not enabled, click Generate Lighting to see the updated lighting effect. |
| Realtime Shadow Color | Define the color used to render real-time shadows. This setting is only available when Lighting Mode is set to Subtractive. |
Lightmapping Settings
Lightmapping Settings are specific to the LightmapperA tool in Unity that bakes lightmaps according to the arrangement of lights and geometry in your scene. More info
See in Glossary backend. Unlike other settings, they’re not shared and have their own parameters. To see full settings information for each lighting system, see documentation on Progressive Lightmapper and EnlightenThe lighting system by Geomerics used in Unity for computing global illumination (GI). More info
See in Glossary.
Other Settings
This section provides documentation for the Other Settings section.
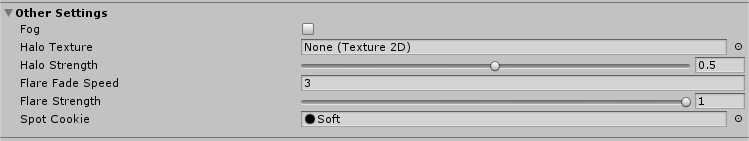
| Property: | Function: | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Other Settings | Settings for fog, HalosThe glowing light areas around light sources, used to give the impression of small dust particles in the air. More info See in Glossary, FlaresThe source asset used by Lens Flare Components. The Flare itself is a combination of a texture file and specific information that determines how the Flare behaves. More info See in Glossary and Cookies. |
|||
| FogA post-processing effect that overlays a color onto objects depending on the distance from the camera. Use this to simulate fog or mist in outdoor environments, or to hide clipping of objects near the camera’s far clip plane. More info See in Glossary |
Enables or disables fog in the Scene. Note that fog is not available with the Deferred rendering path. For deferred rendering, the Post-processing fog effect effect might be suitable. | |||
| Color | Use the color picker to set the color Unity uses to draw fog in the Scene. | |||
| Mode | Define the way in which the fogging accumulates with distance from the cameraA component which creates an image of a particular viewpoint in your scene. The output is either drawn to the screen or captured as a texture. More info See in Glossary. |
|||
| Linear | Fog density increases linearly with distance. | |||
| Start | Set the distance from the Camera at which the fog starts. | |||
| End | Set the distance from the Camera at which the fog completely obscures Scene GameObjects. | |||
| Exponential | Fog density increases exponentially with distance. | |||
| Density | Use this to control the density of the fog. The fog appears more dense as the Density increases. | |||
| Exponential Squared | Fog density increases faster with distance (exponentially and squared). | |||
| Density | Use this to control the density of the fog. The fog appears more dense as the Density increases. | |||
| Halo Texture | Set the Texture you want to use for drawing a Halo around lights. | |||
| Halo Strength | Define the visibility of Halos around Lights, from a value between 0 and 1. | |||
| Flare Fade SpeedA Lighting window property that allows you to set the time (in seconds) over which lens flares fade from view after initially appearing. More info See in Glossary |
Define the time (in seconds) over which lens flaresA component that simulates the effect of lights refracting inside a camera lens. Use a Lens Flare to represent very bright lights or add atmosphere to your scene. More info See in Glossary fade from view after initially appearing. This is set to 3 by default. |
|||
| Flare Strength | Define the visibility of lens flares from lights, from a value between 0 and 1. | |||
| Spot Cookie | Set the Cookie texture you want to use for spot lights. | |||
Debug settings
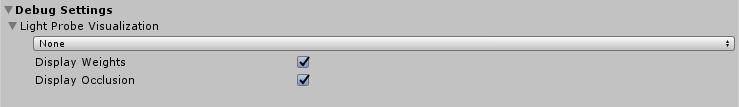
| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| Debug Settings | Settings that help you debug your Scene. |
| Light Probe Visualization | Use this to filter which Light ProbesLight probes store information about how light passes through space in your scene. A collection of light probes arranged within a given space can improve lighting on moving objects and static LOD scenery within that space. More info See in Glossary are visualized in the Scene viewAn interactive view into the world you are creating. You use the Scene View to select and position scenery, characters, cameras, lights, and all other types of Game Object. More info See in Glossary. The default value is Only Probes Used By Selection. |
| Only Probes Used By Selection | Only Light Probes that affect the current selection are visualized in the Scene view. |
| All Probes No Cells | All Light Probes are visualized in the Scene view. |
| All Probes With Cells | All Light Probes are visualized in the Scene view, and the tetrahedrons that are used for interpolationThe estimation of values that determine the shape of an animation curve between two keys. More info See in Glossary of Light Probe data are also displayed. |
| None | No Light Probes are visualized in the Scene view. |
| Display Weights | When ticked, Unity draws a line from the Light Probe used for the active selection to the positions on the tetrahedra used for interpolation. This is a way to debug probe interpolation and placement problems. |
| Display Occlusion | When ticked, Unity displays occlusion data for Light Probes if the Mixed lighting mode is Distance ShadowmaskA version of the Shadowmask lighting mode that includes high quality shadows cast from static GameObjects onto dynamic GameObjects. More info See in Glossary or ShadowmaskA Texture that shares the same UV layout and resolution with its corresponding lightmap. More info See in Glossary. |
Global maps tab
Use the Global maps tab to view the actual textures in use by the lighting system. These include intensity light maps, shadow masks and directionality maps. This is only available when Baked lighting or Mixed lighting is used; the preview is blank for Realtime lighting.
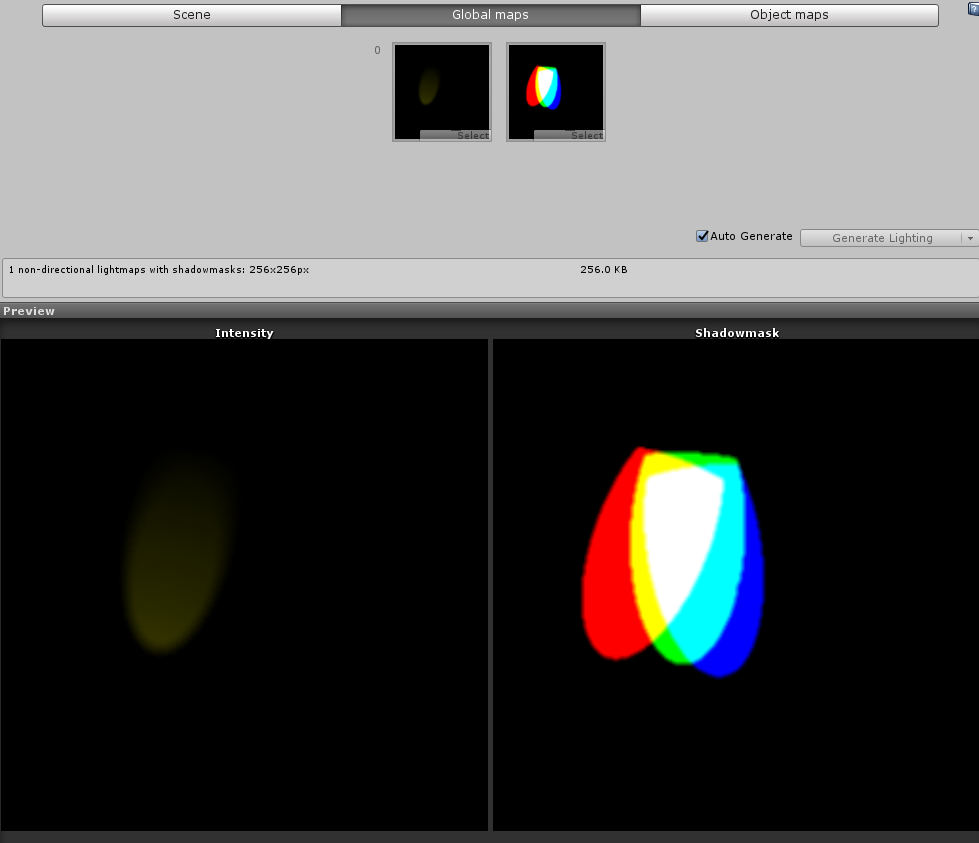
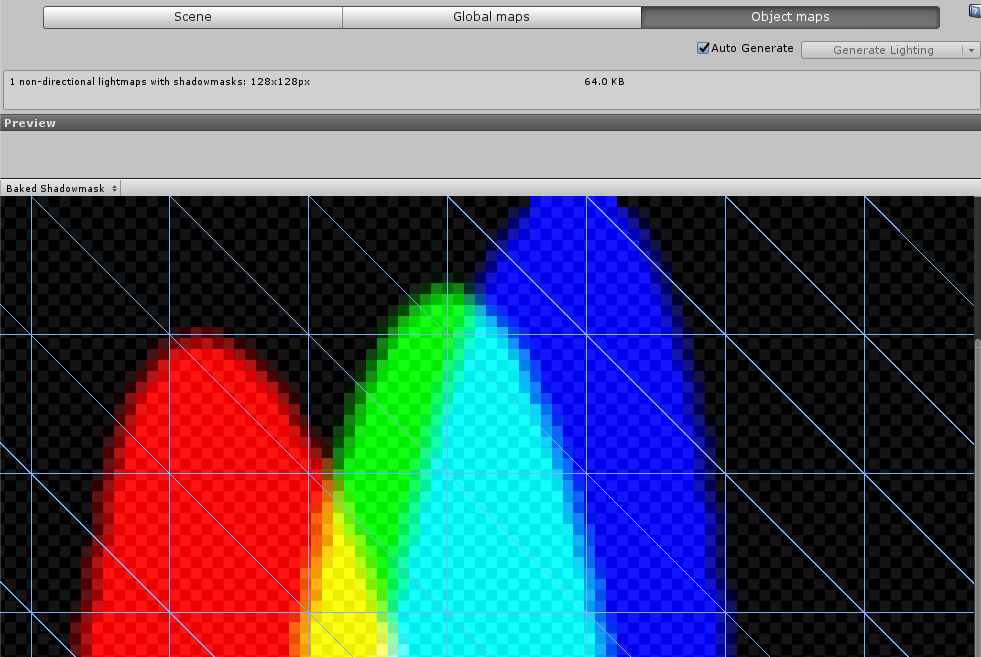
Object maps tab
Use the Object maps tab to see previews of baked textures for the currently selected GameObject only, including shadow masks.
2018–03–29 Page published
Updated in 5.6
Lightmapping section and Debug settings updated in 2018.1 NewIn20181
Did you find this page useful? Please give it a rating: