Creating an Isometric Tilemap
When creating an Isometric Tilemap, there are additional steps to take compared to creating a regular Tilemap. To create an Isometric Tilemap, go to GameObject > 2D Object > Isometric Tilemap/Isometric Z as Y Tilemap.
After creating the Isometric TilemapA GameObject that allows you to quickly create 2D levels using tiles and a grid overlay. More info
See in Glossary, there are additional settings that need to set with the Project and Grid settings for the Isometric Tilemap to be rendered properly.
Custom Axis Sorting
To render the Tiles of an Isometric Tilemap, Tiles placed further to the ‘back’ of the Tilemap need to be rendered first before those in front to create the pseudo-depthA visual simulation of three-dimensional characteristics on a two-dimensional object or environment. This effect is sometimes called “2.5D”. More info
See in Glossary of an isometric perspective. To ensure that all Renderers in the SceneA Scene contains the environments and menus of your game. Think of each unique Scene file as a unique level. In each Scene, you place your environments, obstacles, and decorations, essentially designing and building your game in pieces. More info
See in Glossary conform to this logic, a Custom Axis is used as the Sorting Axis. Set the Transparency Sort Mode to ‘Custom Axis’ and enter (0,1,0) for the XYZ values of the Transparency Sort Axis.
Go to Edit > Project Settings… > Graphics > Camera Settings to set the ‘Custom Axis’ settings.
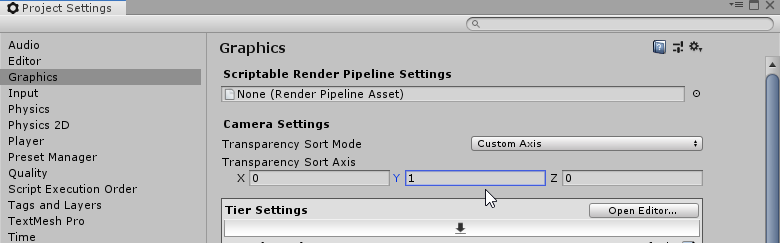
Set the Transparency Sort Axis XYZ values to (0,1,0) to cause all Renderers which are at a higher Y position in the Scene to be rendered first, and appear behind Renderers at a lower Y position.
With the Isometric Z as Y Tilemap, Tiles with different Z-position values are offset along the Y-axis and appear to be at different heights, producing a ‘stacking’ effect with Tiles at the same XY Cell Position. By default, the generic isometric Transparency Sort Axis setting of (0,1,0) does not consider the Tile’s Z-position values during sorting which results in the Tiles being rendered out of intended order (see the example below).
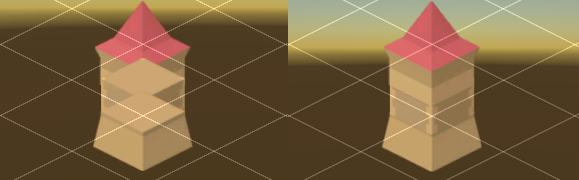
Set the Transparency Sort Axis to (0,1,–0.26) to correctly render Tiles with different Z positions. The Z-axis is set to –0.26 to give a bias to Tiles with higher Z positions to be drawn first.
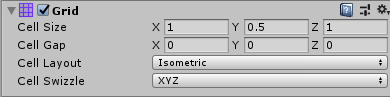
Grid Cell Size settings
| Isometric | Creates an Isometric Tilemap with the default settings. |
| Isometric Z As Y | Creates an Isometric Tilemap where a Tile’s Z-axis value is added to its Y-axis value. This causes the Tile to be visually offset along the Y-axis by that value, creating the illusion of height as the Tiles are placed on the Tilemap. |
Isometric Tilemaps use either dimetric projectionA form of parallel projection where the dimensions of a 3D object are projected onto a 2D plane, and only two of the three angles between the axes are equal to each other. This form of projection is commonly used in isometric video games to simulate three-dimensional depth. More info
See in Glossary or true isometric projectionA form of parallel projection where the dimensions of a 3D object are projected onto a 2D plane, and the angles betwen all three axes are equal to each other. This form of projection is commonly used in isometric video games to simulate three-dimensional depth. More info
See in Glossary parallel projection angles. For more information about the two forms of projection, please refer to this article for further details.
Changing the Cell Size of the Grid component changes the size of angles that make up each Cell, which affects the type of projection being simulated. By default, Cell Size of the Isometric Cell Layout is (1, 0.5, 1) which simulates dimetric projection angles. To simulate true isometric projection angles instead, set the Y value to ‘0.57735’.
- Isometric Tilemaps added in 2018.3 NewIn20183
Did you find this page useful? Please give it a rating: